Plugins
Categories - Jump to: Breakdown | Export | Analysis | Third party
Breakdown
Breakdown plugins - Jump to: Field Breakdown | Two Field Breakdown | Unique Combinations | Polymorphisms | Publication Breakdown | Sequence Bin Breakdown
Field Breakdown
Summary: Breakdown of query results by field
The field breakdown plugin displays the frequency of each value for fields, alleles and schemes. Output is in the form of dynamic charts, maps, and tables. Data can be exported as an Excel file, SVG image, or FASTA file.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
Two Field Breakdown
Summary: Breakdown of one field against another
The two field breakdown plugin generates a table breaking down the frequencies of one field against another. This is analagous to a spreadsheet pivot table. Any primary metadata field, locus, or scheme field can be used and the output can be exported as an Excel spreadsheet.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
Unique Combinations
Summary: Determine frequencies of unique field combinations
The Unique Combinations plugin calculates the frequencies of unique file combinations within an isolate dataset. Primary metadata fields, allele designations and scheme fields can be combined. Results are returned in an Excel spreadsheet.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
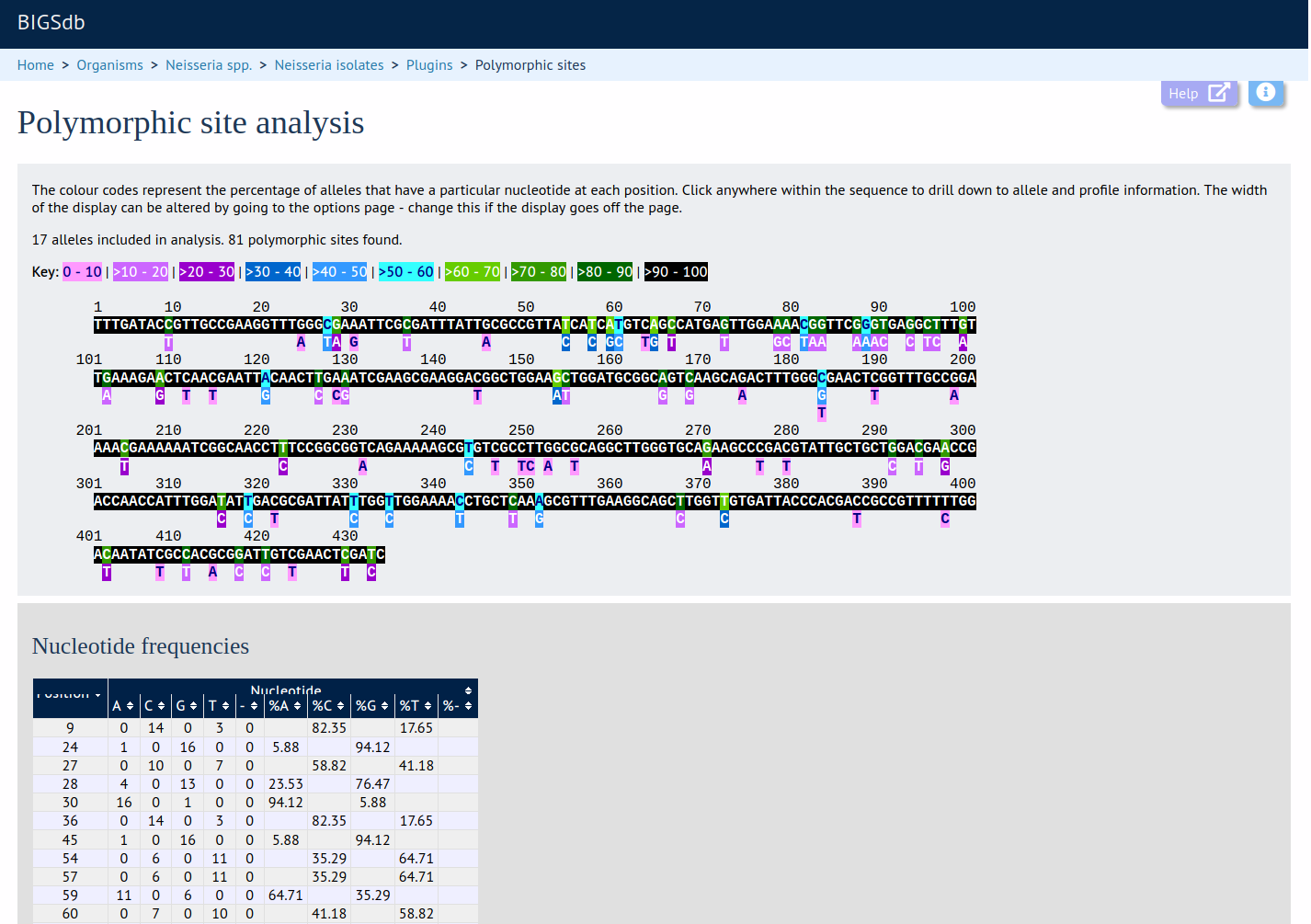
Polymorphisms
Summary: Tool for analysing polymorphic sites for particular locus in an isolate dataset
This plugin generates a schematic of the selected locus showing all the polymorphic sites present in the selected dataset. These are also shown in a tabular form with precise frequencies for each nucleotide at every position.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
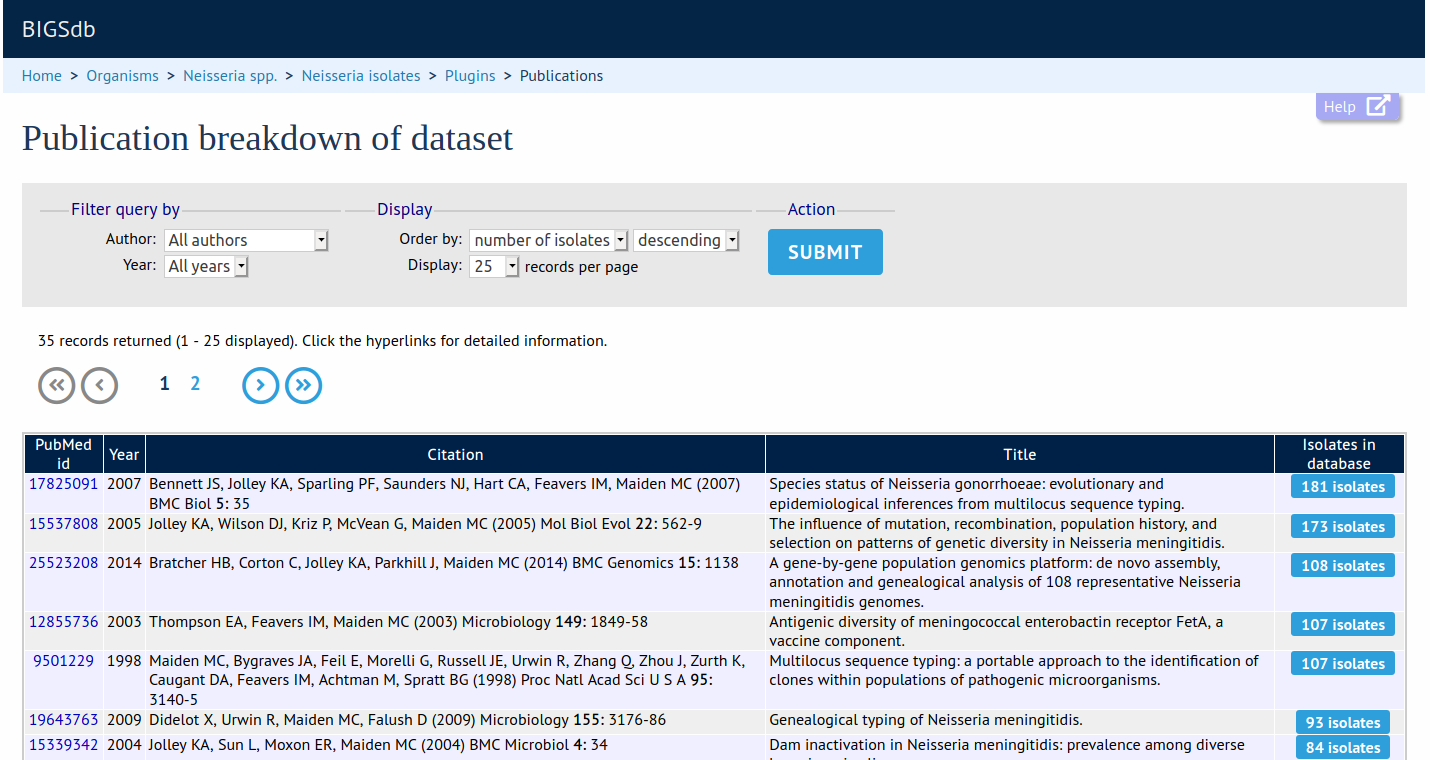
Publication Breakdown
Summary: Breakdown of query results by publication
This plugin shows all publications linked to isolates in a query dataset or within the whole database. The results can be filtered by author or year. The output includes full citation details and a link to display all isolates linked to any listed publication.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
Launch 'Publication Breakdown'
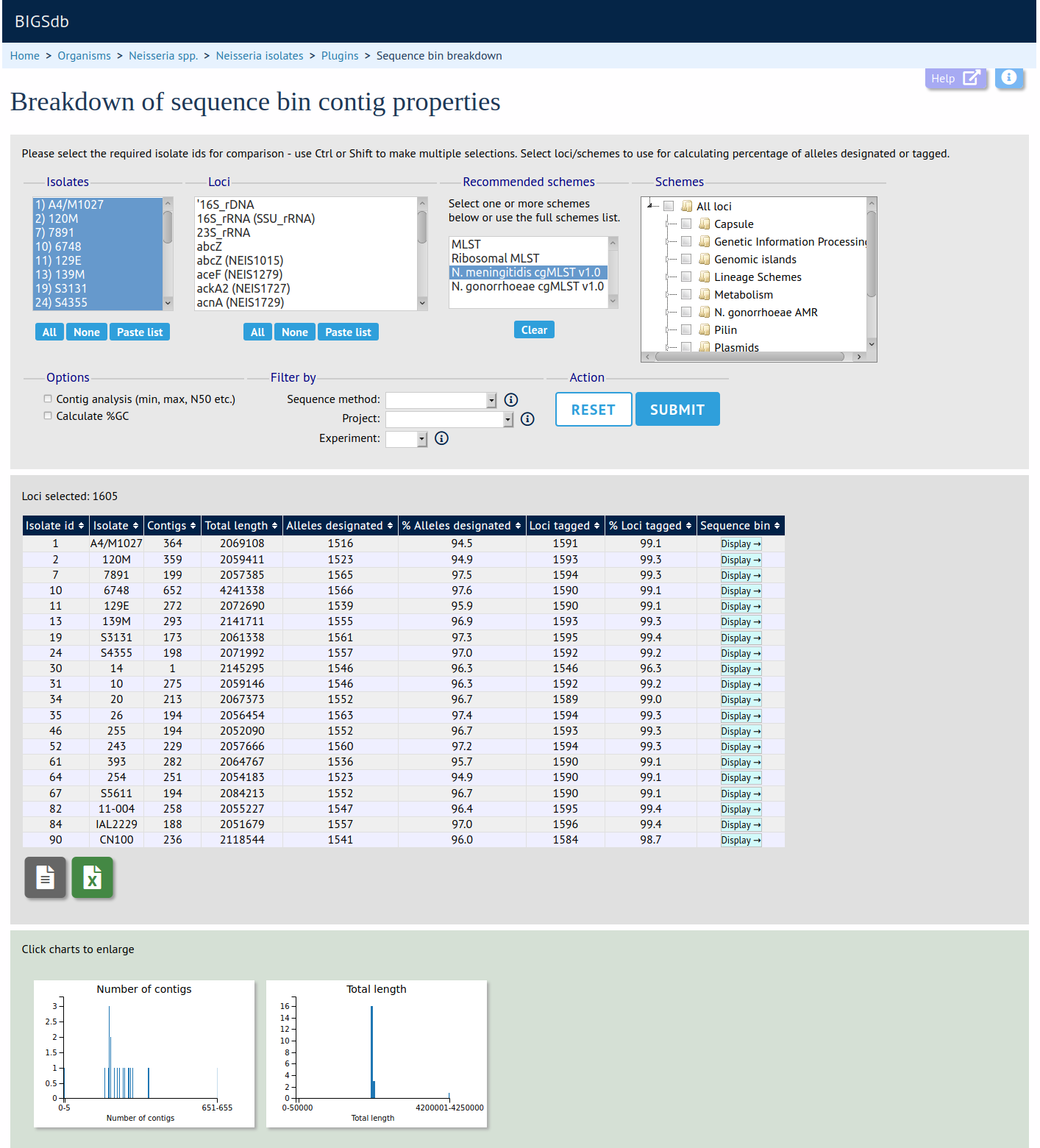
Sequence Bin Breakdown
Summary: Breakdown of sequence bin contig properties
The sequence bin breakdown plugin calculates statistics based on the number and length of contigs in the sequence bin as well as the number of loci tagged for each isolate record. Using this latter metric against a cgMLST scheme can be a good indicator of genome quality. Values for number of contigs, total sequence length, mean contig length and contig length distribution are charted.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
Launch 'Sequence Bin Breakdown'
Export
Export plugins - Jump to: Export | Contig export | Sequence Export
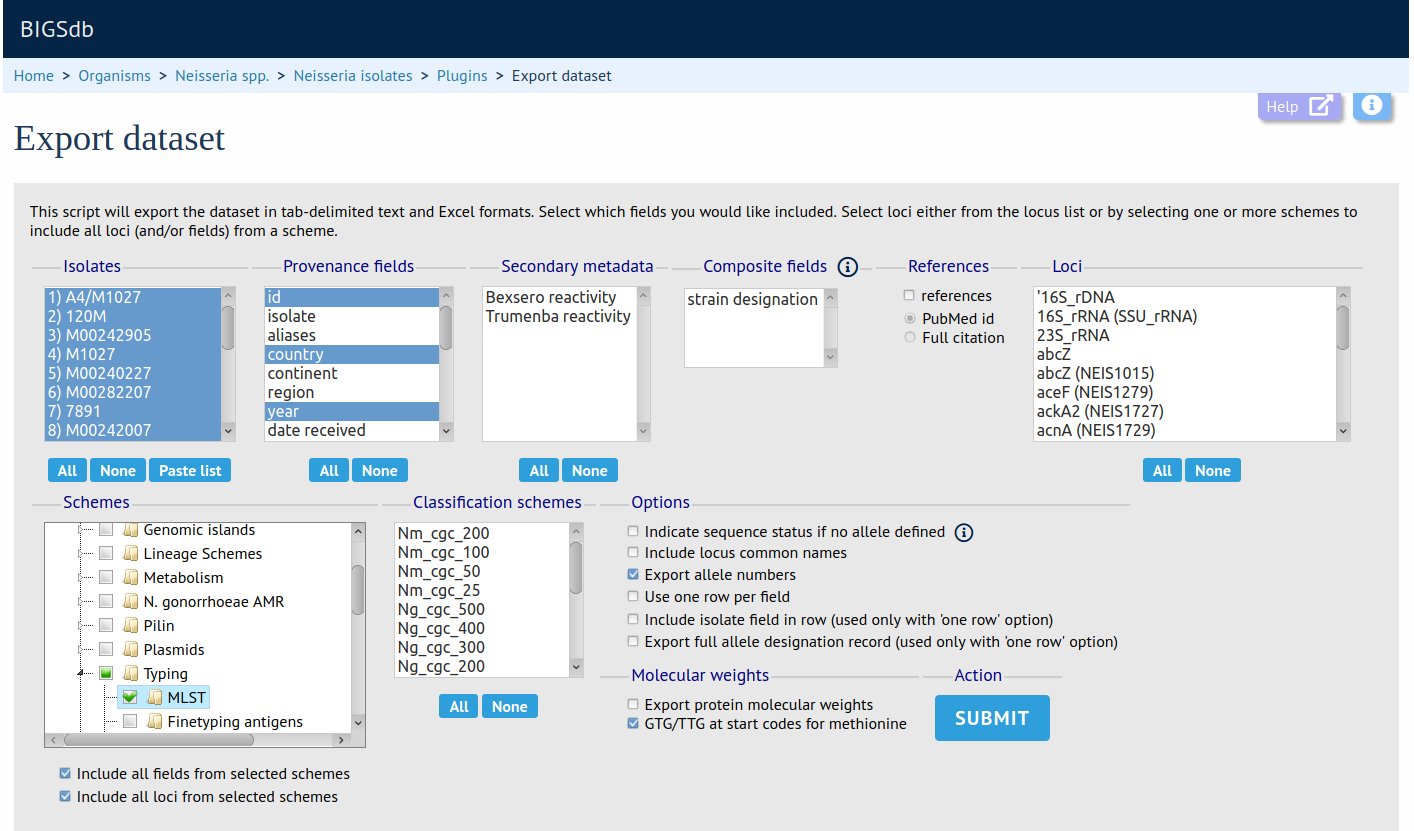
Export
Summary: Export dataset generated from query results
The Export plugin creates a download file of any primary metadata, secondary metadata, allele designations, scheme designations, or publications for isolates within a selected dataset or for the whole database. The output file is in Excel format.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
Contig export
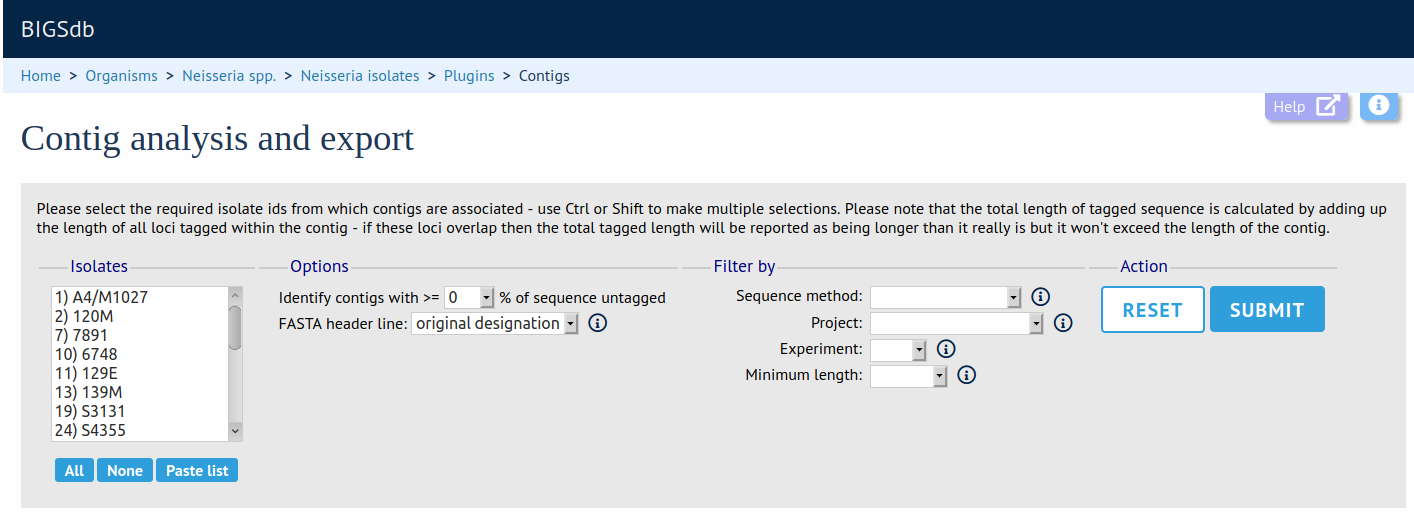
Summary: Analyse and export contigs selected from query results
This plugin enables the contigs associated with each isolate in a dataset to be downloaded in FASTA format. They can also be downloaded in batch mode as a TAR file. The contigs included in the download can be filtered based on the percentage of the sequence that has been tagged with a locus so that poorly annotated regions can be analysed specifically.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
Sequence Export
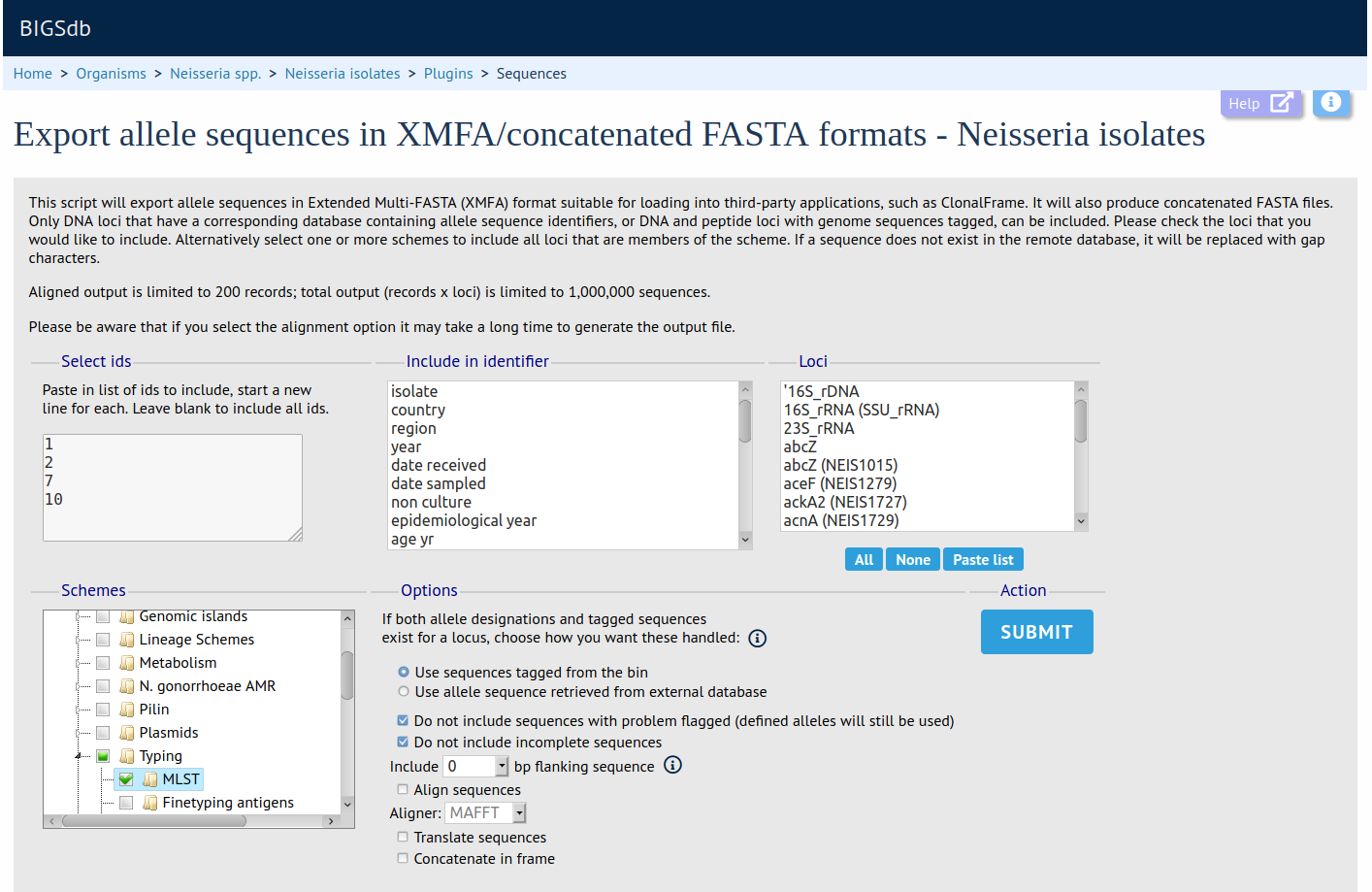
Summary: Export concatenated allele sequences in XMFA and FASTA formats
This plugin creates concatenated XMFA and FASTA files of selected loci for a particular dataset. These sequences can optionally be aligned, using either MAFFT or MUSCLE, facilitating quick analysis of the outputs in third-party phylogenetic analysis packages.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
Analysis
Analysis plugins - Jump to: Codon Usage | Gene Presence | Genome Comparator | BLAST | rMLST species identity
Codon Usage
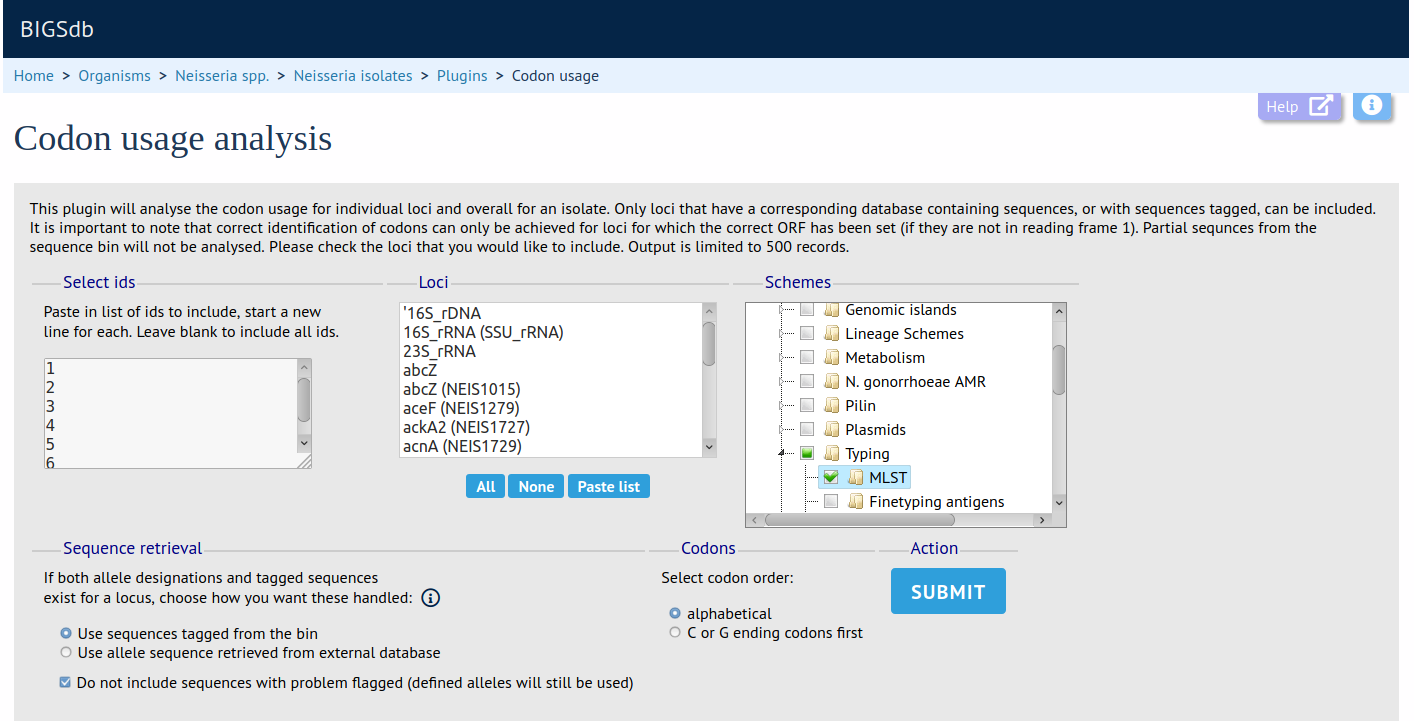
Summary: Determine codon usage for specified loci for an isolate database query
The codon usage plugin calculates the absolute and relative synonymous codon usage by isolate and by locus for any dataset or the whole database. Specific loci or the loci that are members of a particular scheme can be chosen for analysis.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
Gene Presence
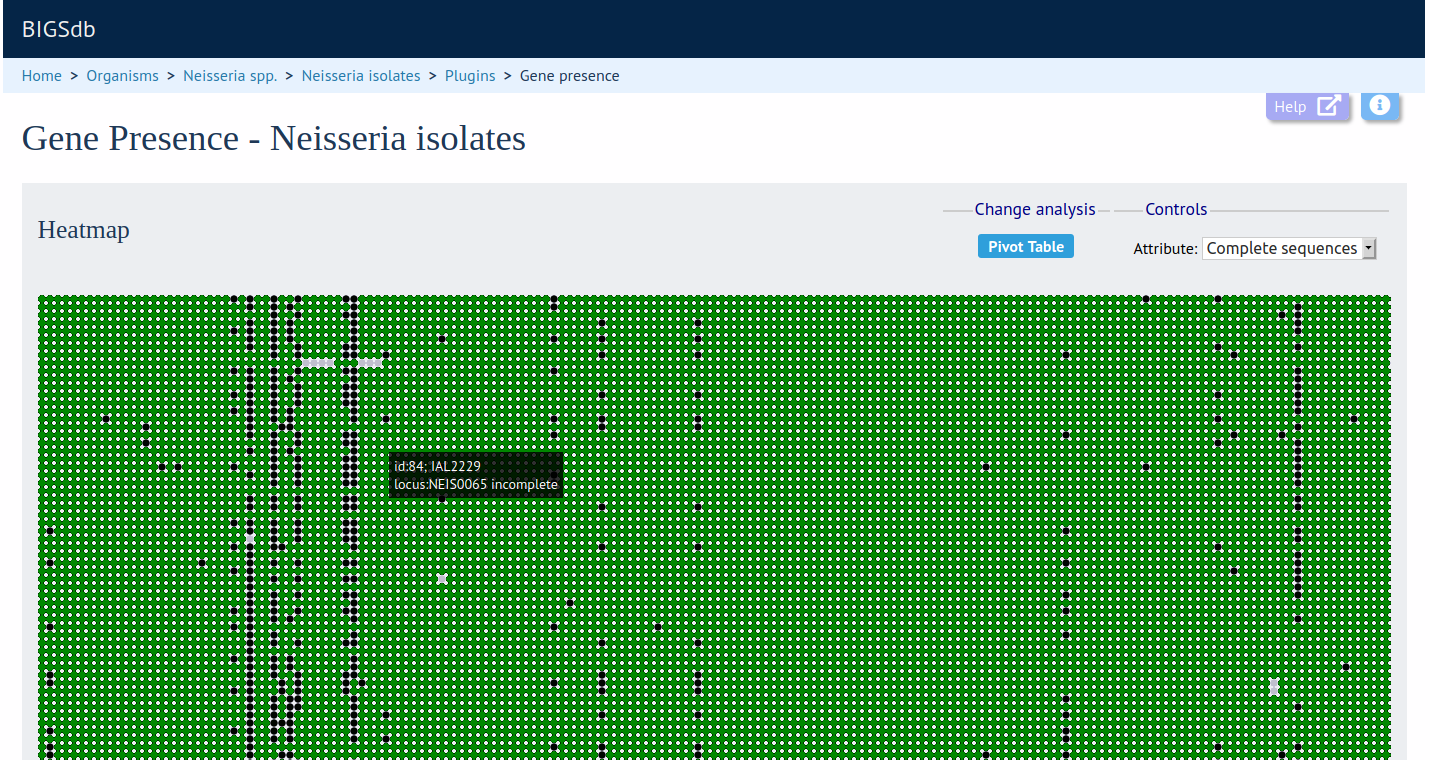
Summary: Analyse presence/absence of loci for dataset generated from query results
The Gene Presence analysis tool will determine whether loci are present or absent, incomplete, have alleles designated, or sequence regions tagged for selected isolates and loci. If a genome is present and a locus designation not set in the database, then the presence and completion status are determined by scanning the genomes. The results can be displayed as interactive pivot tables or a heatmap. The analysis is limited to 500,000 data points (locus x isolates).
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
Genome Comparator
Summary: Compare genomes at defined loci or against loci defined in a reference genome
Genome Comparator is used to compare whole genome data of isolates within the database using either the database defined loci or the coding sequences of an annotated genome as the comparator. Output is equivalent to a whole genome MLST profile, a distance matrix calculated based on allelic differences and a NeighborNet graph generated from this distance matrix. The analysis facilitates the determination of precisely which loci vary among isolates. Additionally, user-uploaded genomes that are not contained in the database can be analysed alongside genomes that are.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
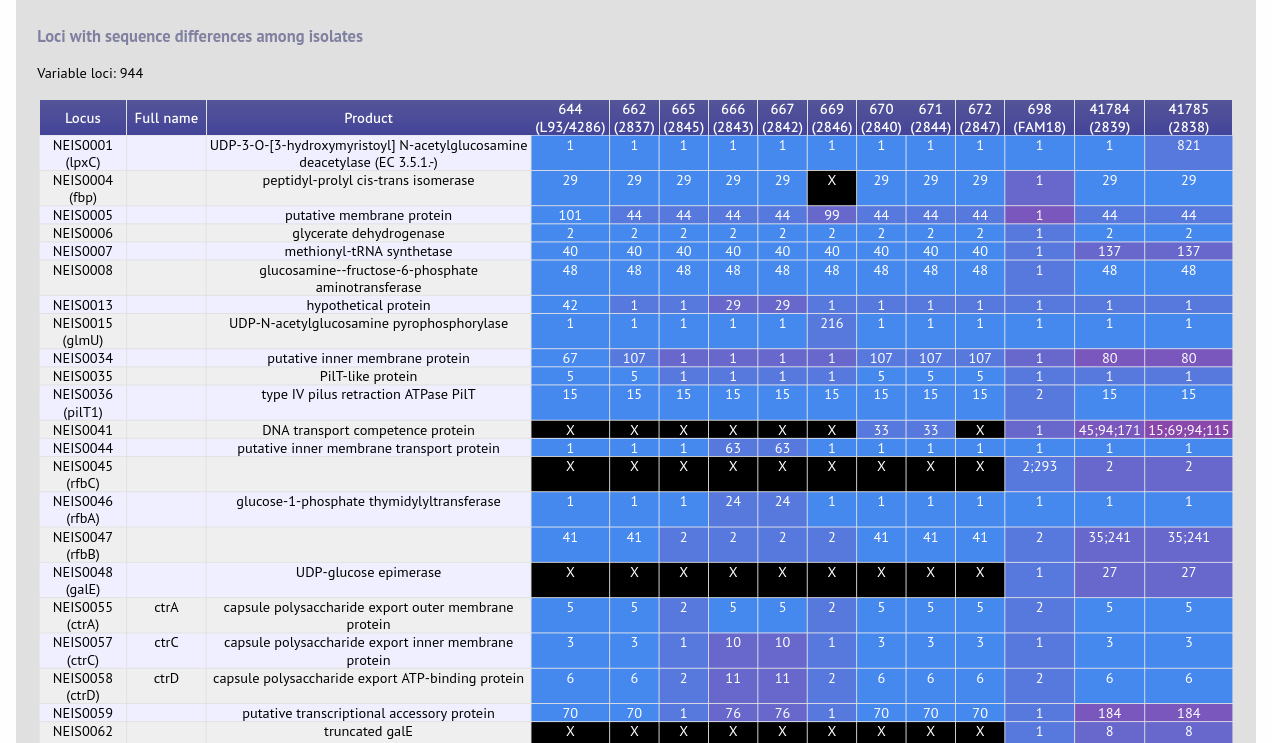
BLAST
Summary: BLAST a query sequence against selected isolate data
The BLAST plugin enables you to BLAST a sequence against any of the genomes in the database, displaying a table of matches which can be downloaded in Excel format. In addition, the matched sequence regions are made available for download in FASTA format, either with or without surrounding flanking sequence.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
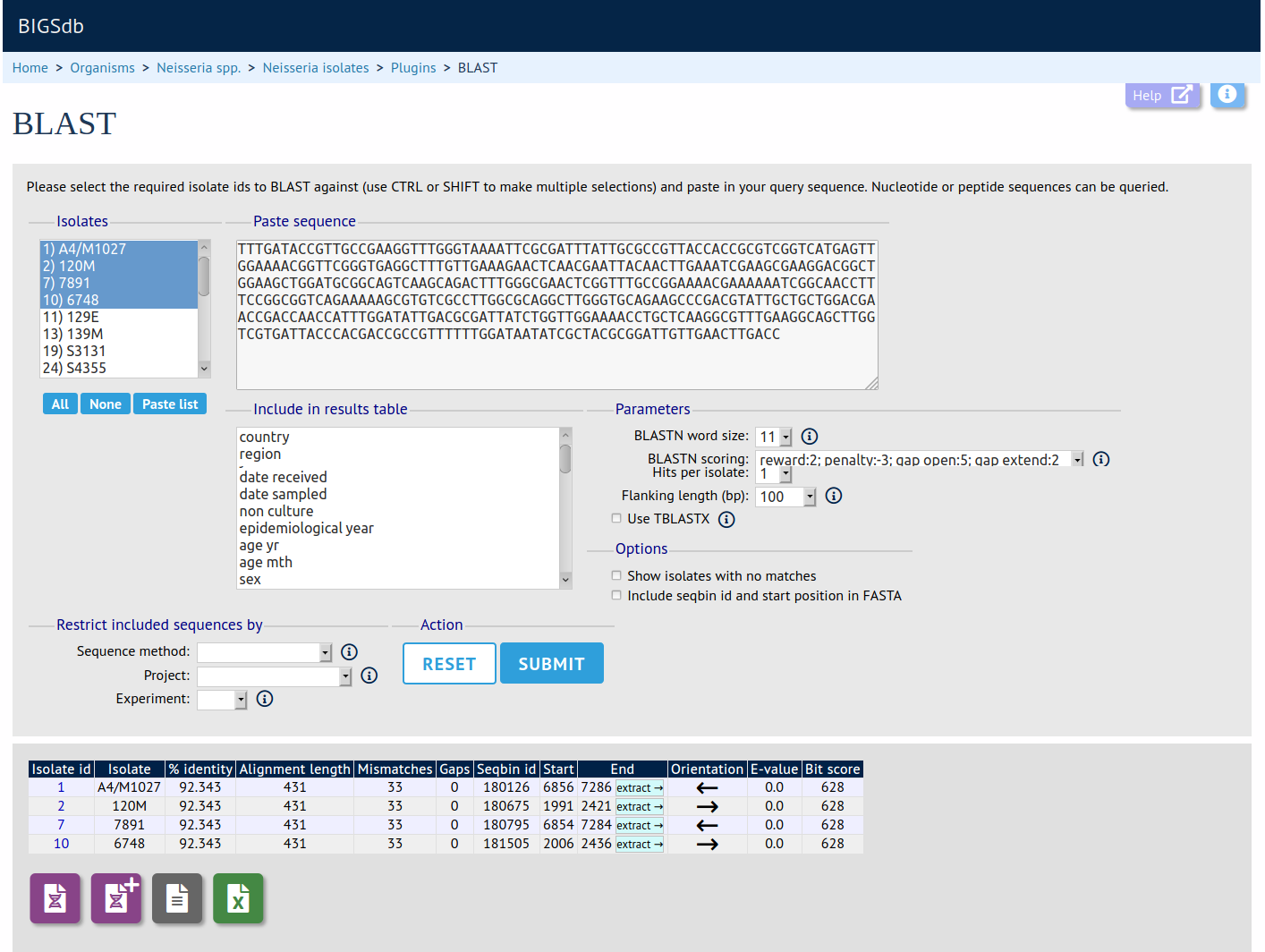
rMLST species identity
Summary: Use rMLST to identify species from bacterial genome assemblies
The species identification tool extracts ribosomal MLST alleles from genomes and determines the species based on the count of alleles that are uniquely found within a single species (or higher taxonomic rank if alleles unique to a species are not found). This is done by making a query via the PubMLST RESTful API to the rMLST typing database.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
Launch 'rMLST species identity'
Third party
Third party plugins - Jump to: GrapeTree | iTOL | PhyloViz | ReporTree
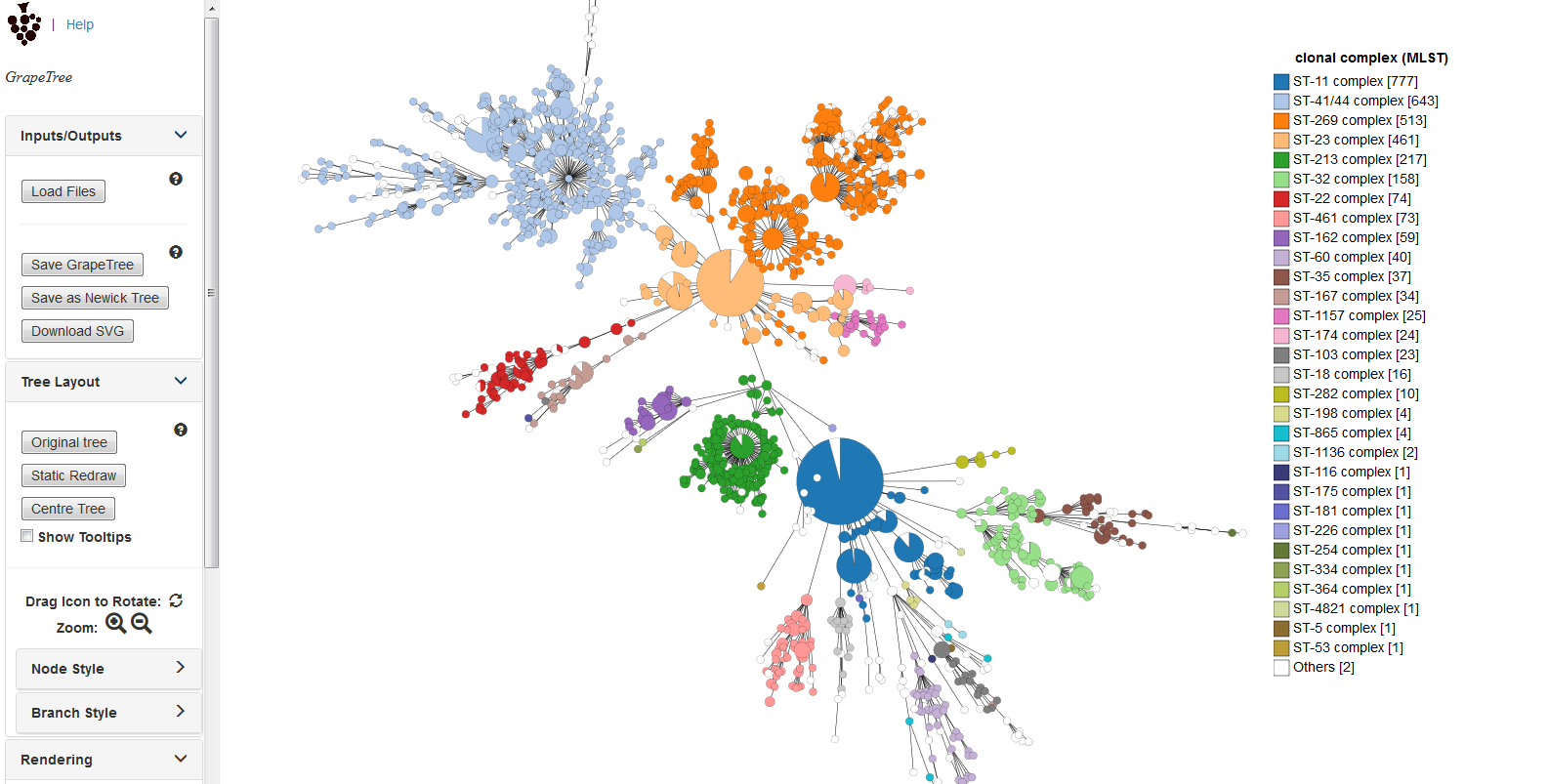
GrapeTree
Summary: Visualization of genomic relationships
GrapeTree is a tool for generating and visualising minimum spanning trees (Zhou at al. 2018 Genome Res 28:1395-1404). It has been developed to handle large datasets (in the region of 1000s of genomes) and works with 1000s of loci as used in cgMLST. It uses an improved minimum spanning algorithm that is better able to handle missing data than alternative algorithms and is able to produce publication quality outputs. Datasets can include metadata which allows nodes in the resultant tree to be coloured interactively.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io

iTOL
Summary: Phylogenetic trees with data overlays
The ITOL plugin allows you to generate and visualise phylogenetic trees calculated from concatenated sequence alignments of selected loci (or the loci belonging to a particular scheme). Currently, only Neighbour-joining trees are supported. Datasets can include metadata which allows nodes in the resultant tree to be coloured. Datasets are uploaded to the Interactive Tree of Life website (Letunic & Bork 2016 Nucleic Acids Res 44(W1):W242-5) for visualisation.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
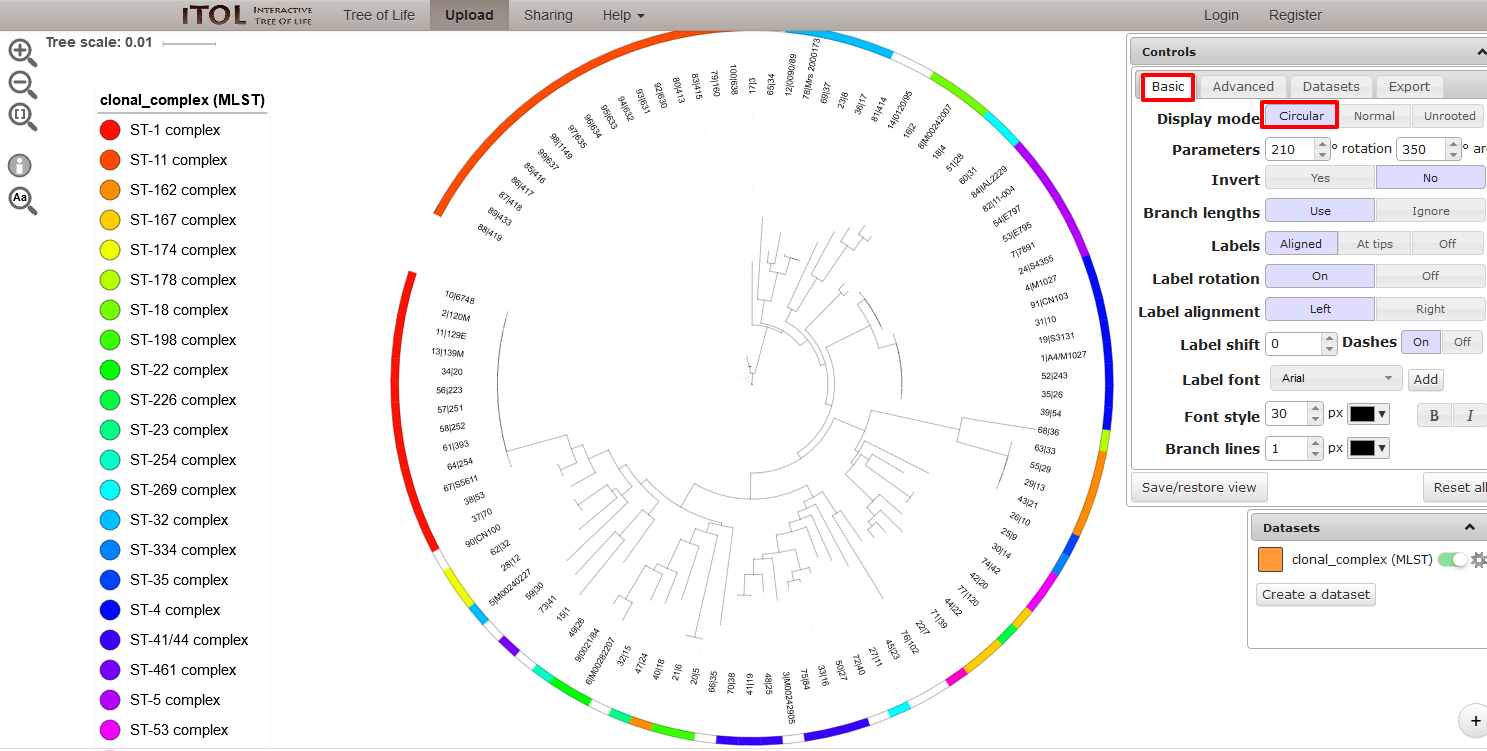
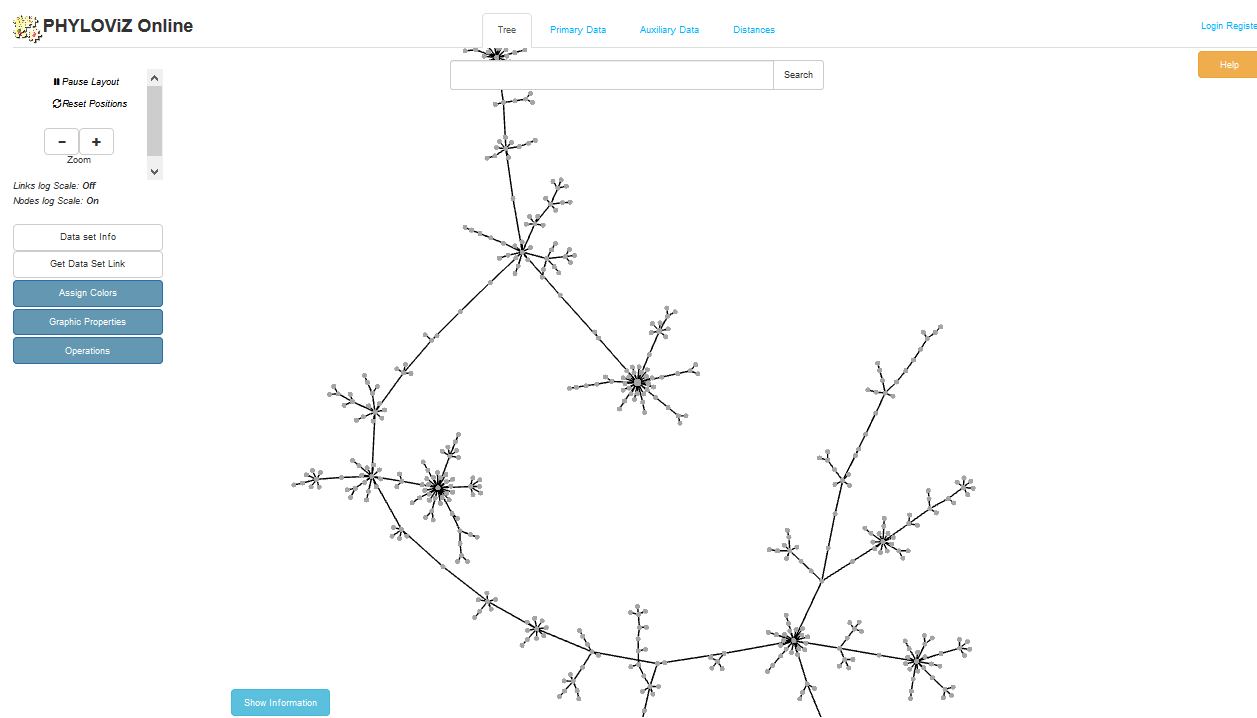
PhyloViz
Summary: Creates phylogenetic inference and data visualization for sequence-based typing methods
PhyloViz Online is a tool for generating and visualising minimum-spanning trees based on allelic profiles. This plugin generates datasets that are then uploaded to PhyloViz Online for visualisation. Datasets can include metadata which allows nodes in the resultant tree to be coloured interactively.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io
ReporTree
Summary: Surveillance-oriented tool to strengthen the linkage between pathogen genetic clusers and epidemiological data
A pivotal outcome of genomics surveillance is the identification of pathogen genetic clusters/lineages and their characterization in terms of geotemporal spread or linkage to clinical and demographic data. This task usually relies on the visual exploration of (large) phylogenetic trees (e.g. Minimum Spanning Trees (MST) for bacteria or rooted SNP-based trees for viruses). As this may be a non-trivial, non-reproducible and time consuming task, we developed ReporTree, a flexible pipeline that facilitates the detection of genetic clusters and their linkage to epidemiological data. It is described in Mixão et al. 2023 Genome Med 15:43.
Documentation bigsdb.readthedocs.io