Data access policy note: since January 1st, 2025, registration and authentication are mandatory to access all data curated after this date, either via the web interface or via the application programming interface (API authentication help link).
To request an API key, follow the steps outlined at: Requesting a BIGSdb-Pasteur API Key
Please contact us if you have any questions.
Genome Quality Check and the “QC status” field
QC criteria:
Starting from January 2023, genomes must comply with the following QC criteria (Table 1), defined in the scope of the KlebNET-GSP consortium, in order to be imported into the BIGSdb Klebsiella database.
Table 1. KlebNET-GSP quality criteria
| Criteria | Method | Accepted critera | Rejected criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contamination check | conFindr,kmerFinder,kraken2… | < 5% contamination | > 5% contamination |
| Species identification | Kleborate | acceptable identity | Weak identity |
| Genome quality - Number of contigs | arbitrary threshold | ≤ 500 contigs | > 500 contigs |
| Genome quality - Genome size | mean ±2SD | [4,969,898; 6,132,846] bp | < 4,969,898 or > 6,132,846 bp |
| Genome quality - GC content | mean ±2SD | [56.35; 57.98] %GC | < 56.35% OR > 57.98% GC |
QC status:
The “QC status” field was added to the isolate fields (Figure 1) to record the QC metrics of genomes, in particular for those deposited into the database before the systematic application of the KlebNET QC criteria. The QC criteria proposed by the KlebNET-GSP consortium were applied to all genomes in the database in January 2023, and a QC status code was defined for each genome.
Figure 1. Example of isolate SB20 (id 10) with a QC status

The QC status is encoded as a 4-digit code (e.g., 0000), each position corresponding to a specific metric in this order: Species, number of contigs, genome size and %GC. To build the QC status code, a score corresponding to valid, rejected, or inconclusive criteria is attributed to each metric:
Code explanations:
0: valid criteria
1: rejected criteria (too many contigs, genome size or %GC below the lower limit)
2: rejected criteria (genome size or %GC above the higher limit)
x: inconclusive criteria (this happens for species check, as rMLST species identification can display multiple results, for instance, e.g., due to genome contamination)
Table 2 provide example QC codes and their interpretations.
NB. Only good quality genomes (QC status: 0000) are used by curators to designate novel alleles, profiles and LIN codes. Submissions of genomes that fail the QC may be entirely rejected.
Table 2. Example of QC codes and their interpretations
| QC status | Species | Contigs number | Genome Size | %GC | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Valid genome (KLEBNET-GSP QC-passed) |
| 0011 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Genome size too small and low %GC |
| 1122 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | Not a Klebsiella, too many contigs, genome size too big and high %GC |
| 1111 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Not a Klebsiella, too many contigs, genome size too small and low %GC |
| x100 | x | 1 | 0 | 0 | Species not verified or validated, too many contigs |
Internal assembly checks:
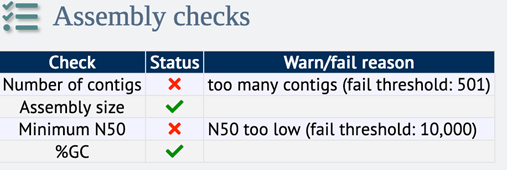
Since November 2022, BIGSdb includes a built-in tool to check contiguity metrics of assembly data. The assembly checks are displayed on the isolate’s information page:
Figure 2. Example of assembly check status for a high-quality genome
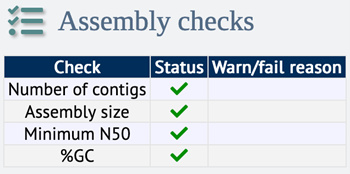
Figure 3. Example of assembly check status for a low-quality genome
rMLST species identification:
The rMLST species identification tool is used to verify the taxonomic designation of the isolates by extracting ribosomal MLST alleles from genomes (Bray et al., 2022, Ribosomal MLST nucleotide identity (rMLST-NI), a rapid bacterial species identification method: application to Klebsiella and Raoultella genomic species validation). The highest taxonomic rank that can be reliably identified, e.g. species, the taxon and its full taxonomy are displayed on the isolate’s information page. An indication of the confidence for the result will also be displayed - this is based on the proportion of alleles found that are unique to a taxon.
Figure 4. Example of rMLST species identification: K. pneumoniae
